When you apply for a loan, a cellphone or any number of other activities, lenders and potential creditors will look at your credit score to help gauge your financial stability and thus the risk of you defaulting on a financial responsibility. The better your credit score is, the higher your chances are for getting approved.

There are many different types of credit scores, but the FICO® score is the most common credit scoring model today and the one used by most lenders.
FICO scores range from 300 to 850 points. Typically, a credit score is considered:
- “Fair” if it’s more than 650.
- “Good” if it’s more than 700.
- “Excellent” if it’s more than 750.
The primary factors that affect your credit score include payment history, the amount of debt you owe, how long you've been using credit, new or recent credit, and types of credit used. Each factor is weighted differently in your score.
Let's take a closer look at the factors that make up your FICO credit score and the importance of each in how the model calculates your score.
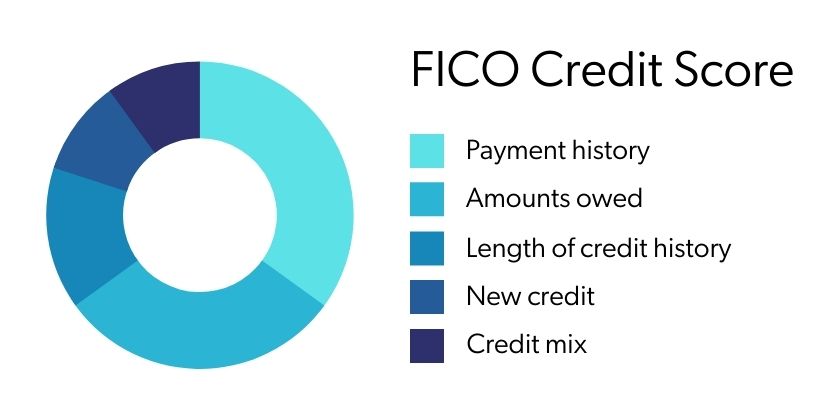
Payment History
Weight: 35%
Payment history defines how consistently you've made your payments on time. This is the most important contributor to your credit score.
Amounts You Owe
Weight: 30%
The amounts you owe is the outstanding debt you currently owe. The lower the amount of outstanding debt, the higher the credit score.
Length of Your Credit History
Weight: 15%
Your credit history is based on the length of time you've had credit accounts open in your name. A longer credit history can help your credit score. If you've had a credit card open for a long time, it makes good sense to continue using that card responsibly to maintain a good score.
New Credit You Apply For
Weight: 10%
Also known as credit inquiries, the pursuit of new credit negatively affects your score.
Every time you apply for credit, your score goes down. There is one exception: when you're shopping for a mortgage, student or auto loan, credit scoring models only count one inquiry if your comparison shopping with multiple lenders is done within a 14- to 45-day period.
For example, if you're shopping for a car and apply for financing at three different car dealerships, your score will not decrease three times; it will only decrease once during the shopping window. That could vary depending on the type of loan you're seeking and the credit scoring model used.
Note that inquiries will affect your credit even if you're denied or ultimately decide against the loan or credit card. Each inquiry affects most people's score by less than 5 points and can stay on your report for up to 24 months.
Types of Credit You Use
Weight: 10%
Your score can increase if you responsibly use different types of credit, such as installment and revolving debt. Even so, it's not necessary to have many different types of credit to have a good credit score.
Last reviewed: December 01, 2025
My Home in your inbox
Sign up to receive resources, tools and tips about buying, owning, refinancing, selling and renting a home in your inbox.